Binary Tree & Graph
2018
A project composed of two data structures, a self-balancing binary tree (AVL Tree) and a Graph. Complete with expected methods and some specific operations like Dijkstra algorithm.
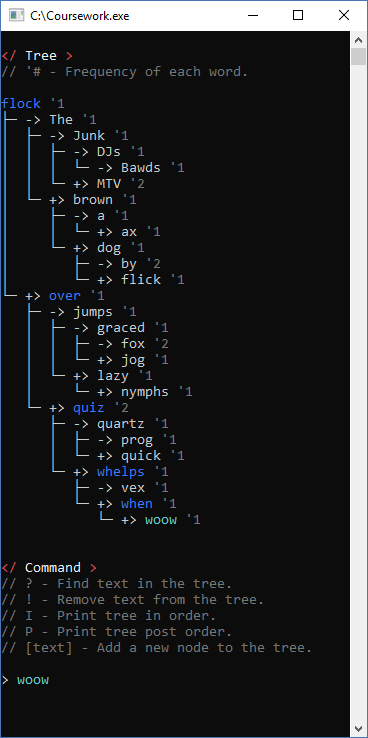
Binary Tree
For this project I needed to build a binary tree data structure, with add, remove, find and print methods. After doing that I decided to take it a step forward and make it a self-balancing tree, this way reducing the worst case big-O to O(log(n)).
Self-Balancing
Uses three functions to balance the tree, the first checks the balance of a specific subtree, the second function just checks what the depth for a node should be and the last function actually balances the tree, after checking if it is Right Right Heavy, Right Left Heavy, Left Left Heavy or Left Right Heavy and adjusts it accordingly.
if (balance < -1) // Left Heavy
{
int childBalance = checkBalance(node->left);
// Left Right Heavy
/* T -> R
/ -> / \
O -> O T
\ ->
R -> */
if (childBalance > 0)
{
shared_ptr<BinaryTreeNode> tempLeftRight = node->left->right;
if (tempLeftRight->left)
tempLeftRight->left->parent = node->left;
if (tempLeftRight->right)
tempLeftRight->right->parent = node;
node->left->right = tempLeftRight->left;
tempLeftRight->left = node->left;
node->left = tempLeftRight->right;
tempLeftRight->right = node;
if (shared_ptr<BinaryTreeNode> parent = node->parent.lock())
(parent->left == node ? parent->left : parent->right) = tempLeftRight;
else
root = tempLeftRight;
tempLeftRight->parent = node->parent;
tempLeftRight->left->parent = tempLeftRight;
node->parent = tempLeftRight;
tempLeftRight->depth = getCorrectDepth(tempLeftRight);
tempLeftRight->left->depth = getCorrectDepth(tempLeftRight->left);
}
...
}
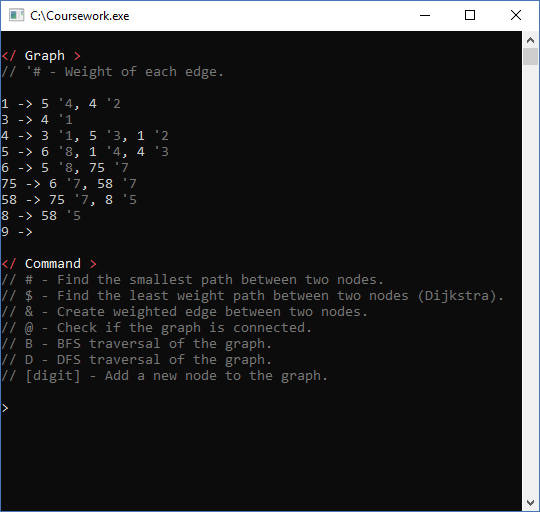
Graph
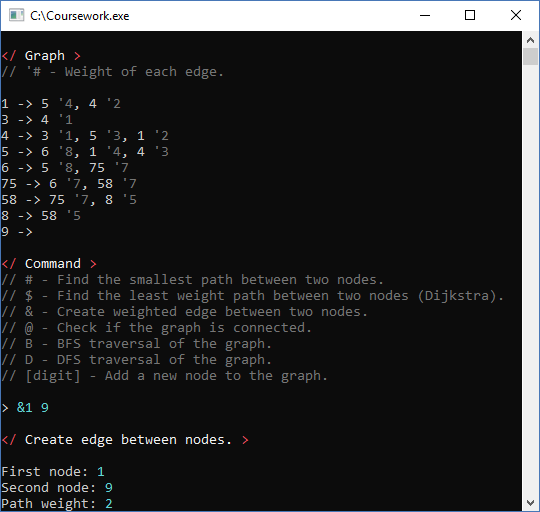
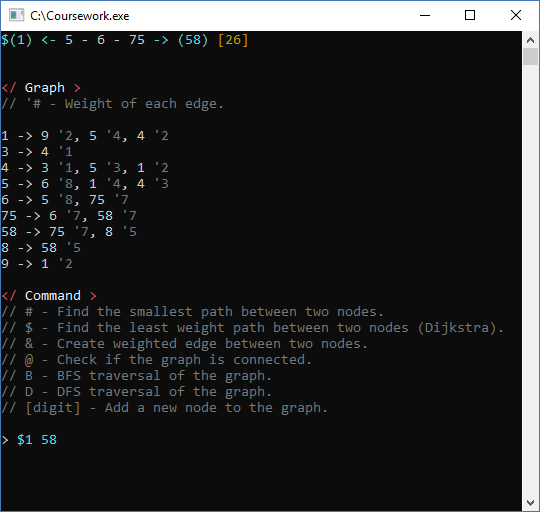
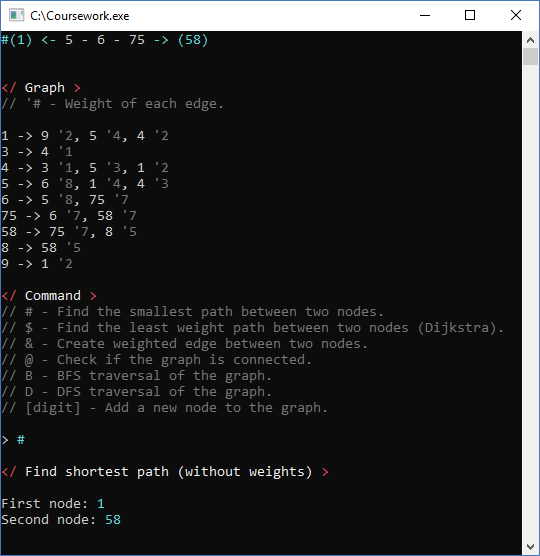
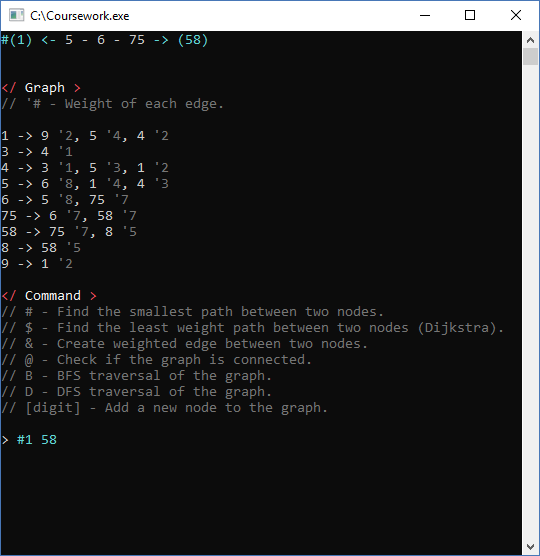
The graph required methods like, add node, add edge, check if there’s a path, Dijkstra best path, check if the graph is connected and print methods. I decided to use an adjacency list for the edges because it was going to work with sparse graphs and a matrix would consume more memory. Each edge is also an object where both nodes hold a pointer to, instead of having to update both nodes for any changes it can be made on the Edge object.
Dijkstra
This is a straight forward use of the algorithm, for each node creates a DijkstraItem object an sets the cost to the maximum allowed number, after steps trough each node finding and keeping track of the cheapest path to it, until it gets to the destination. After check if it is connected from the start node to the end node and prints the path
///<summary>Data structure used by Dijkstra algorithm.</summary>
struct DijkstraItem
{
weak_ptr<GraphNode> fromRef;
size_t cost;
bool visited;
///<summary>Creates a new item, with cost 0 and visited set to false.</summary>
///<remark>BigO notation for worst case is O(1).</remark>
DijkstraItem()
{
this->cost = UINT64_MAX;
visited = false;
}
///<summary>Creates a new item, with the given properties.</summary>
///<remark>BigO notation for worst case is O(1).</remark>
///<param name="fromRef">Pointer to the node from where this was found.</param>
///<param name="cost">Cost to get from the starting node to this one, throught the 'fromRef'.</param>
DijkstraItem(shared_ptr<GraphNode> fromRef, size_t cost)
{
if (!fromRef)
throw invalid_argument("'fomrRef' can't be null.");
this->fromRef = fromRef;
this->cost = cost;
visited = false;
}
};
Testing
All methods of all classes on the project are tested, from wrong input to check if properties are set accordingly and operations run as they should.
Reflection
Some of the functions end up with a big-O of O(n^2) because the program tries to save memory in some places and as the graph isn’t dense the iterations can be done relatively fast, for denser graphs other methods could be used.
The custom queue, stack and list work as a singly linked list to save memory, for improved processing speed a hash table or a binary tree would be better used.
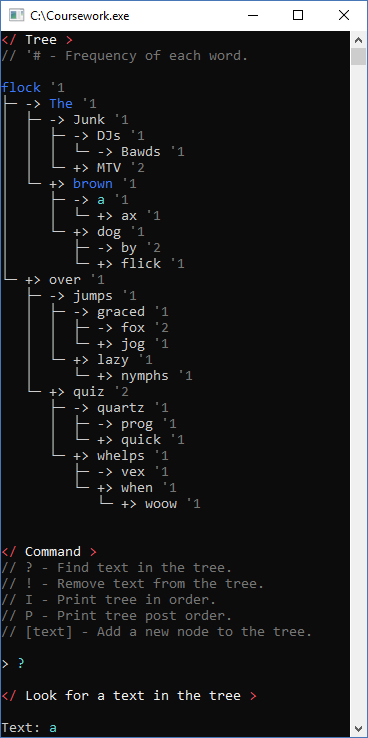
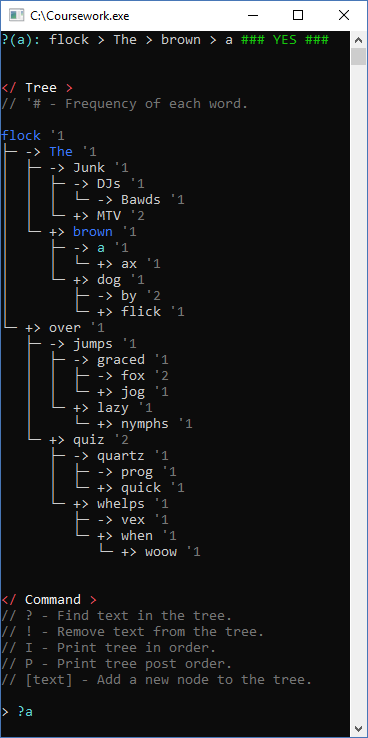
Screenshots